The Most Impactful Recent Manufacturing Solutions in Automotive Manufacturing

Ben Austin is the founder and CEO of multi-award-winning digital…
Contents
ToggleThe automotive manufacturing industry has always been at the forefront of innovation, and recent advancements in manufacturing solutions have pushed the sector even further into the realm of efficiency, sustainability, and precision. From autonomous vehicles to electric car production, the industry is experiencing a rapid transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. In this article, we will explore the most impactful recent manufacturing solutions that are shaping the future of automotive production, improving quality, reducing costs, and enabling a more sustainable industry.
1. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has revolutionized automotive production by allowing manufacturers to create complex parts and components with higher precision, faster turnaround times, and less waste compared to traditional methods. By using 3D printing, automakers can prototype new designs quickly and efficiently, reducing the time required for product development.
Key Benefits:
- Faster Prototyping: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping of car parts, allowing designers to test and refine their ideas before committing to large-scale production.
- Complex Geometries: With additive manufacturing, manufacturers can produce intricate, lightweight designs that would be impossible or cost-prohibitive using traditional methods.
- Cost Reduction: It can lower costs by reducing material waste and minimizing the need for expensive tooling or molds.
Recent examples of 3D printing in automotive manufacturing include the use of 3D printed parts in production vehicles, such as interior components, brackets, and other non-structural elements. Companies like Ford and BMW have embraced additive manufacturing for everything from prototype parts to tools and production aids.
2. Robotics and Automation
Robotics has long been an integral part of automotive manufacturing, but recent advancements in robotic technology have made it more efficient, flexible, and cost-effective. Modern robots are now capable of performing highly specialized tasks with greater precision, such as painting, welding, assembly, and material handling.
Key Benefits:
- Precision and Accuracy: Robots can perform repetitive tasks with high precision, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing the risk of human error.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Advanced robotics systems are now more adaptable, capable of working on multiple types of vehicles or parts without needing to be retooled.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Robots can work around the clock, increasing production capacity while reducing the need for manual labor, which can cut costs and increase overall efficiency.
For example, Tesla has invested heavily in robotics and automation to streamline production, particularly in the assembly of their electric vehicles (EVs). Robots play a key role in the assembly lines, performing tasks such as welding, bolting, and placing heavy components.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are increasingly being integrated into automotive manufacturing processes to enhance productivity, optimize production schedules, and improve decision-making. These technologies allow manufacturers to collect and analyze data in real-time, identifying potential issues before they become significant problems.

Key Benefits:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can monitor equipment performance and predict when machines are likely to fail, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Production Optimization: Machine learning algorithms can analyze production data to identify inefficiencies and recommend improvements, optimizing workflows and resource allocation.
- Quality Control: AI systems can also be used for quality control, inspecting parts for defects and ensuring that only the highest-quality components make it to the final assembly line.
General Motors (GM) has employed AI to streamline its manufacturing process, particularly in predictive maintenance, where AI models analyze data from sensors embedded in equipment to forecast when maintenance is needed. This helps GM avoid unexpected machine failures and production delays.
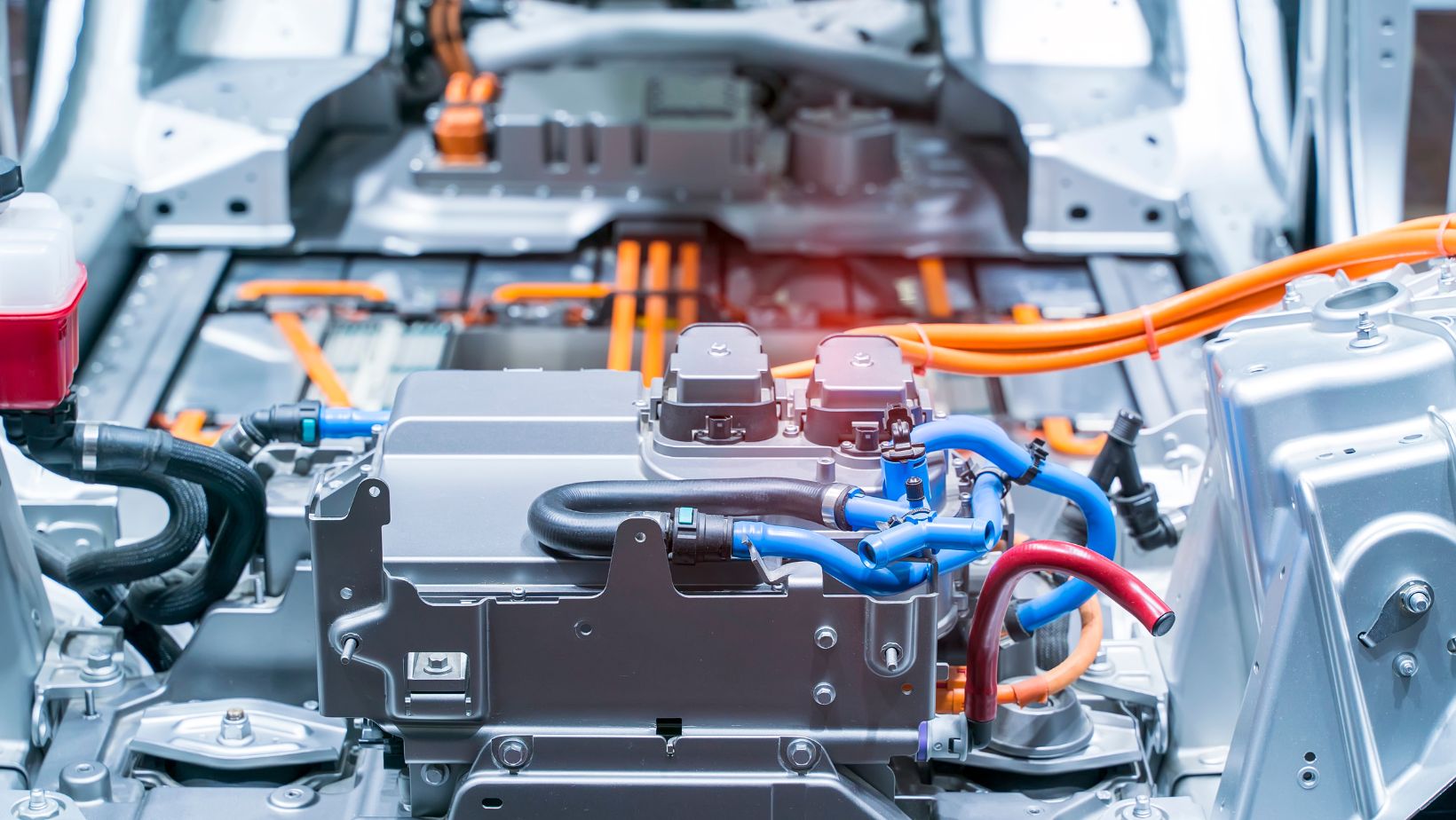
4. Electric Vehicle (EV) Production Solutions
The automotive industry’s shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) is one of the most significant transformations in recent years, and new manufacturing solutions are emerging to meet the growing demand for EVs. From battery manufacturing to assembling electric drivetrains, automakers are investing in specialized equipment and techniques to streamline EV production.
Key Benefits:
- Battery Manufacturing: With the rise of EVs, automakers are developing specialized manufacturing processes for producing high-performance batteries. Companies like Volkswagen and Tesla are building “gigafactories” that integrate the production of batteries and vehicles in a single location, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Sustainability: EV production solutions focus on reducing emissions and improving energy efficiency, aligning with the industry’s goal of reducing its carbon footprint.
- Supply Chain Innovations: The global demand for EVs has driven innovations in the supply chain, particularly in sourcing materials for batteries, such as lithium and cobalt, ensuring that supply chains are optimized and sustainable.
Automakers such as Ford and BMW are also accelerating the transition to EV production by utilizing digital technologies like digital twins (virtual simulations of physical processes) to improve the efficiency of their assembly lines and to better integrate sustainable practices into their EV manufacturing processes.
5. Connected and Smart Factories
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has led to the development of smart factories that are connected through networks of sensors and devices. These factories allow manufacturers to collect data at every stage of production, enabling them to make real-time adjustments and improvements.
Key Benefits:
- Real-Time Data: Connected factories can provide real-time data on production performance, supply chain logistics, and even employee safety.
- Automation and Efficiency: With connected devices, machines can automatically adjust to ensure the highest efficiency and quality during production.
- Supply Chain Transparency: IoT devices track parts, tools, and materials throughout the supply chain, reducing waste and ensuring that the right components are delivered at the right time.
One example of this is BMW’s smart manufacturing plants, where sensors and data analytics are used to monitor everything from energy consumption to assembly line performance. This connectivity helps the company make more informed decisions and streamline its production processes.
Conclusion
The automotive manufacturing industry is experiencing a wave of innovation driven by advanced technologies like robotics, AI, 3D printing, and smart manufacturing solutions. These advancements are not only helping manufacturers produce vehicles faster and at a lower cost but are also improving product quality, enhancing sustainability, and enabling the shift toward electric vehicles.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of automotive manufacturing will undoubtedly feature even more sophisticated solutions that drive efficiency and keep manufacturers competitive in an increasingly global market.
What's Your Reaction?
Ben Austin is the founder and CEO of multi-award-winning digital marketing agency Absolute Digital Media. Ben loves to write and share exclusive insights into the world of digital marketing from his own eyes.



