The Impact of Anoxic Brain Injury on Cognitive Function
The brain requires a constant supply of oxygen to function correctly. Any disruption can lead to brain damage. After an anoxic brain injury, the primary concern is to restore oxygen to the brain and prevent any further damage through medical care. Treatment also includes physical, occupational, and speech therapy to help you regain your pre-injury abilities.
Memory Loss
The brain requires a steady and uninterrupted supply of oxygen to carry out essential biochemical processes. When this flow of nutrients is disrupted, anoxic brain injury can occur.
Survivors of anoxic brain injury can experience cognitive problems, including memory loss, difficulty thinking and problem-solving, and altered communication skills. Movement disorders can also result from anoxic brain damage and include abnormal movements and a lack of coordination and balance.
Some brain areas are more sensitive to anoxia than others, particularly the hippocampus (important for memory), cerebellum, and basal ganglia. Patients with anoxic brain injury tend to move from vegetative states at a slower rate than those with traumatic brain injuries.
Medical treatment will focus on restoring the flow of oxygen to the brain and controlling seizures and other problems that might arise from the injury. A CT or MRI scan will help doctors identify any signs of brain swelling and determine the extent of the injury. Medications may be given to reduce swelling and to control blood pressure and heartbeat.
Difficulty with Attention
A severe anoxic brain injury can result in difficulty concentrating. It can impact daily activities, including social behaviors and safety judgment. It may also affect the ability to work or attend school.
Cognitive impairments from anoxic brain damage can also affect problem-solving skills, coordination, and emotions. Family members must understand these challenges to encourage recovery and support the patient appropriately.
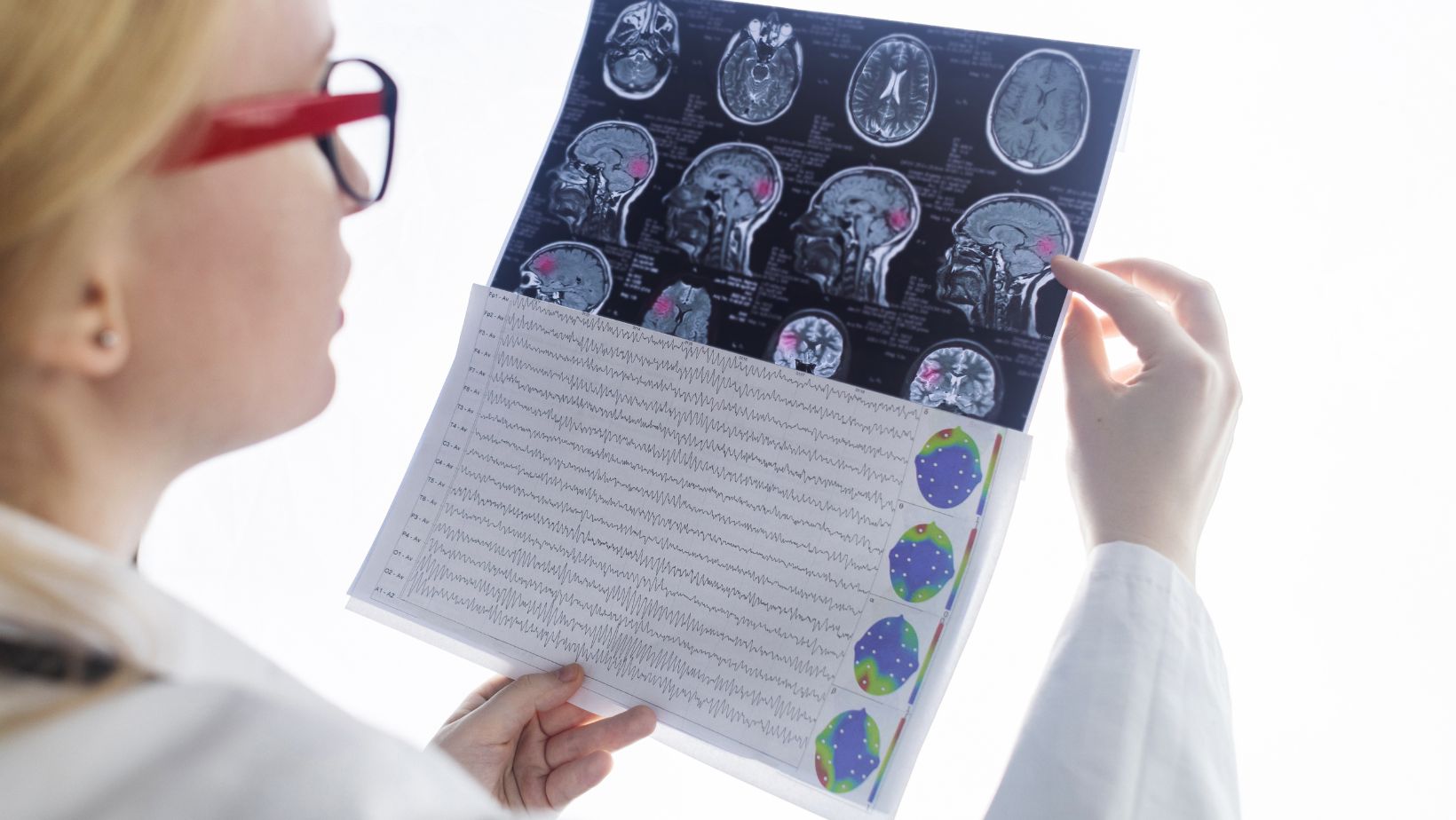
Several diagnostic methods play an essential role in assessing the extent of anoxic brain injury. Tools like MRI, GCS, EEG, and SSEPs help medical professionals gather critical information about the importance of the injury and determine the best course of treatment for the patient. Those who receive immediate care and have minimal damage to the cerebral cortex or basal ganglia can often recover cognitive abilities with time. However, those who suffer from a severe anoxic brain injury often remain in a coma or vegetative state. They may open their eyes but cannot respond or communicate with others.
Language Disorders
Many people who suffer from global anoxic brain injury will struggle with a variety of linguistic problems. These can include a lack of ability to remember words, difficulty selecting the correct word, mixing up similar words or phrases, and having trouble understanding commonly used terms.
These cognitive issues can impact the quality of a person’s speech and their ability to interact with others. Global anoxic brain injury can also cause a condition called transcortical motor aphasia, which is an impairment of the movement patterns involved in speaking.
Having the support of family and friends is essential when caring for someone who has suffered anoxic brain damage. In addition, it is vital to participate in a holistic program of rehabilitation that includes physiotherapy and occupational therapy for movement disorders, as well as a speech-language pathologist to address the challenges related to linguistic deficits. The more committed and patient a person is during this process, the greater their chance of fully recovering.
Movement Disorders
A person with anoxic brain injury may experience movement disorders, such as tremors or spasticity. It can affect balance and coordination, making it challenging to complete simple tasks. Damage to the basal ganglia may result in abnormal movements like athetosis or chorea.
The death of brain cells due to anoxia interrupts electrochemical impulses and interferes with the function of neurotransmitters – chemical messengers that relay signals throughout the body and influence behavior. These include the chemicals serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which regulate moods; oxytocin, which increases pleasure and decreases pain; and acetylcholine, which plays a vital role in memory.
Getting immediate care and staying informed about treatment options can help you support your loved one through recovery from anoxic brain injury.
What's Your Reaction?
Deepak is a lover of nature and all things sporty. He loves to spend time outdoors, surrounded by the beauty of the natural world. Whether he's hiking, biking, or camping, Deepak enjoys being active and in touch with nature. He also loves to compete and push himself to his limits. Deepak is an avid cyclist, runner, and swimmer. He has competed in several triathlons and marathons, and is always looking for new challenges to take on.


